Fast and fierce reportedly influenced Qualcomm’s naming for their next-generation chipsets and associated programs for mobile platforms. Qualcomm’s “Smarter, Faster, Better” marketing emphasis fortifies “fast and fierce” within its Snapdragon Spaces Pathfinder Program, launched to assist Augmented Reality (AR) developers “in accelerating the transition from smartphone to head-worn AR.” CareAR has Joined Qualcomm’s Snapdragon Spaces Pathfinder Program to speed the adoption of hands-free use cases capable of supporting CareAR’s innovative augmented reality with vendor-independent wearable agility.
The adoption of hands-free smart glasses for augmented reality applications has been somewhat limited to date but is expected to accelerate. Snapdragon benefits are contributing to the expected growth ramp with chipset support for head-mounted Display (HMD) vendors to improve performance, reduce heat, and enable more ergonomic comfort.
ABI Research in their 37 Technology Stats You Need to Know in 2023 forecasts approximately 20 million XR device shipments in 2023. Fueling this wearables growth is “enterprise value in training and remote worker enablement” along with “increasing consumer availability and demand”.
CareAR’s early access to Snapdragon technology available by joining Qualcomm’s Snapdragon Spaces Pathfinder Program provides the essential element of augmented reality HMD user engagement for training and remote worker enablement deployments. Performance combined with wearable ease of use and comfort will result in a greater proliferation of hands-free AR use cases across a broad range of industry segments.
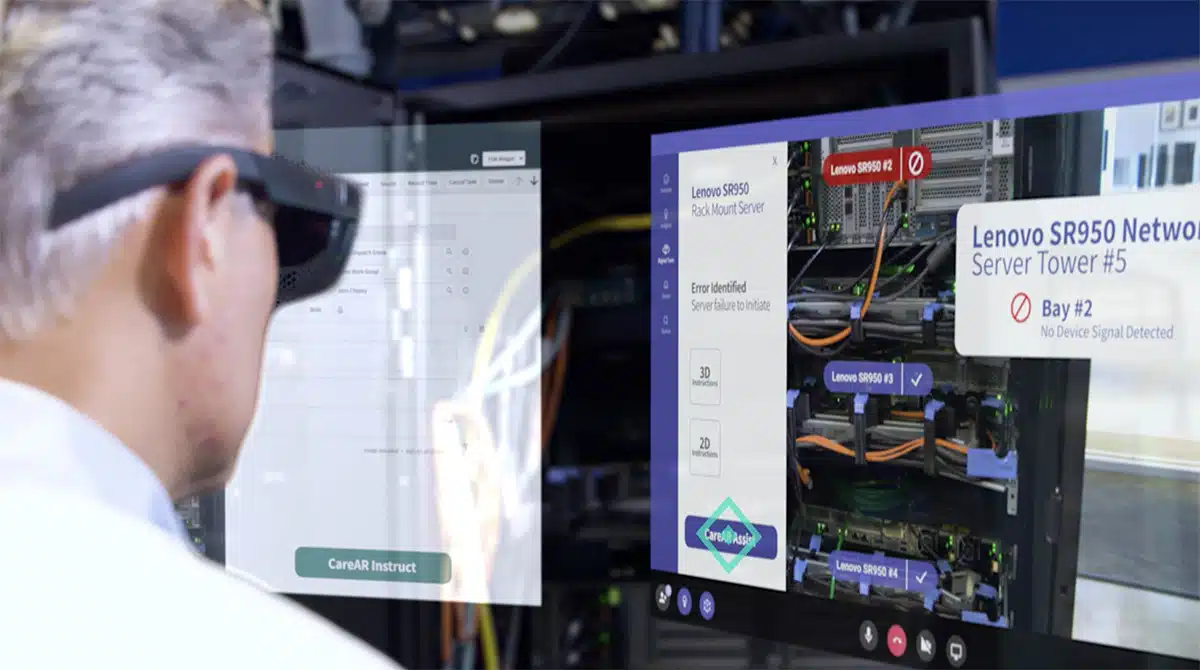
A stand-out example of how CareAR is now using Snapdragon technology with head-worn glasses is via Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) support for AR user interface benefits. CareAR remote assist and self-guidance applications utilize SLAM to engage users with innovative graphical guidance overlayed on actual equipment. Real-time anchored annotations remain in place despite head movement. Most HMD vendors today do not support SLAM due to processing power and other challenges.

Lenovo ThinkReality A3 Smart Glasses
CareAR is partnering with co-Snapdragon Spaces partner Lenovo, an HMD vendor using the Snapdragon chipset that now supports SLAM with their ThinkReality A3 wearables. ThinkReality A3 with CareAR enables powerful hands-free use cases such as inspection step-by-step guidance that precisely overlays graphical directions locked in place to ensure inspection accuracy and safety.
Gesture control is another benefit that CareAR early Snapdragon technology access is being applied for user experience benefits. CareAR’s inherently rich annotation palette of graphical guidance tools can now be tuned for hands-free use, contributing to enthusiastic HMD user adoption for CareAR® Instruct and CareAR® Assist.
The Snapdragon Spaces Pathfinder Program encourages vendor-independent support for capable new augmented reality technology that will accelerate adoption for wearable use cases. The most critical driver however is how augmented reality applications take advantage of new HMD capabilities such as what Snapdragon offers.
For those considering visual remote assistance and self-solve, it’s important to remember that augmented reality and digital twin guidance and training applications are all not created equal. Fundamental benefits of anchoring rich graphical guidance in virtual space, and the ability to automatically verify that an Instruct user has appropriately completed an action with computer vision are AR examples that extend well beyond a simple video stream to take HMD workflows to a new level.
CareAR above referenced benefits spotlights the “rubber meets the road” value now becoming attainable with Snapdragon hands-free acceleration for wearables. As we move forward, smart glasses will quickly evolve to adapt to user demands with comfort, ease of use, and processing power. Augmented reality software capabilities however are the critical drivers for use case success and business value. CareAR’s innovative augmented reality solutions spanning smartphones, tablets, and increasingly wearables expand the horizon for self-solve and remote assist visual engagement for many more use cases across all industry segments.